Cell Meter Annexin V凋亡检测试剂盒 橙色荧光 适合流式细胞检测
| Ex (nm) | 557 | Em (nm) | 570 |
| 分子量 | - | 溶剂 | - |
| 存储条件 | - |
我们的Cell Meter 检测试剂盒是一套用于检测细胞生存力的工具,有多种参数可用于检测细胞活力。 该特定试剂盒旨在通过测量磷脂酰丝氨酸(PS)的转运来检测细胞凋亡。 在细胞凋亡中,PS转移到质膜的外部小叶。 磷脂酰丝氨酸在细胞表面的出现是细胞凋亡初始/中间阶段的普遍指标,可以在观察形态变化之前进行检测。该试剂盒使用与PS特异性结合的荧光膜联蛋白V。 已经证明膜联蛋白V缀合物选择性结合PS。 使用带有575/26 nm发射滤光片组(PE通道)的流式细胞仪,优化了该特定的测定试剂盒以监测细胞凋亡。百萤生物是AAT Bioquest的中国代理商,为您提供优质的Cell Meter Annexin V凋亡检测试剂盒。
适用仪器
| 流式细胞仪 | |
| Ex: | 488 nm or 532 nm |
| Em: | 575/26 nm |
| 通道: | PE 通道 |
样品实验方案
简要概述
- 用测试化合物制备细胞(200 µL /样品)
- 添加膜联蛋白V-iFluor 555测定溶液
- 在室温下孵育30至60分钟
- 使用带有575/26 nm滤光片(PE通道)的流式细胞仪或带有Cy3滤光片组的荧光显微镜分析细胞
实验步骤
1.用膜联蛋白V-iFluor 555准备和孵育细胞:
1.1用测试化合物处理细胞一段时间(对于用星形孢菌素处理过的Jurkat细胞,需要4-6小时)以诱导细胞凋亡。
1.2离心细胞以获得1-5×105细胞/管。
1.3将细胞重悬于200 µL分析缓冲液(组分B)中。
1.4向细胞中加入2 µL Annexin V-iFluor 555(组分A)。
1.5避光保存,于室温下孵育30至60分钟。
1.6在使用流式细胞仪或荧光显微镜分析细胞之前,添加300 µL分析缓冲液(组分B)以增加体积。
1.7使用带有575/26 nm滤光片(PE通道)的流式细胞仪或带有Cy3滤光片组的荧光显微镜检测荧光强度。
2.通过使用流式细胞仪进行分析:
2.1使用带有575/26 nm滤光片的流式细胞仪(PE通道)定量Annexin V- iFluor 555结合物。
3.通过使用荧光显微镜进行分析:
3.1孵育后用移液管吸移细胞悬液,用测定缓冲液冲洗1-2次,然后用测定缓冲液重悬细胞。
3.2将细胞添加到载玻片盖玻片的载玻片上。注意:对于贴壁细胞,建议直接在盖玻片上生长细胞。与Annexin V-iFluor 555孵育后,用测定缓冲液冲洗1-2次,然后将测定缓冲液加到盖玻片上。将玻片上的盖玻片倒置并可视化细胞。与膜联蛋白V-iFluor 555孵育后,还可以将细胞固定在2%甲醛中,并在显微镜下观察。
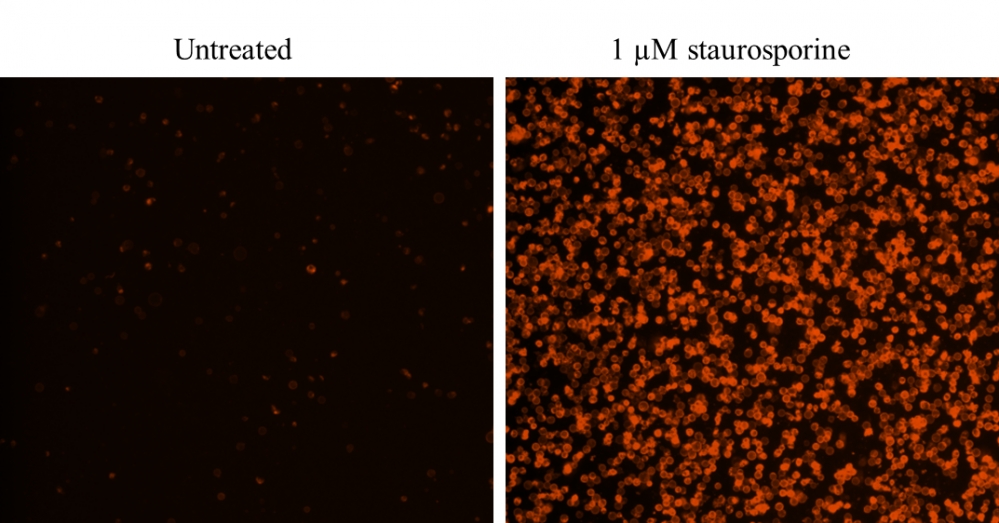
3.3在荧光显微镜下使用Cy3滤光片组,用Annexin V-iFluor 555分析凋亡细胞。将Nuclear Red DCS1(#17552)添加到细胞后,使用Cy5通道测量细胞活力。质膜上的橙色染色表明膜联蛋白V-iFluor 555与细胞表面的PS结合。
参考文献
In situ polymerizable hydrogel incorporated with specific pathogen-free porcine platelet-rich plasma for the reconstruction of the corneal endothelium
Authors: Lin, Yung-Kai and Sharma, Ruchi and Ma, Hsu and Chen, Wen-Shyan and Yao, Chao-Ling
Journal: Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers (2017)
Novel regulations of MEF2-A, MEF2-D, and CACNA1S in the functional incompetence of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells by induced indoxyl sulfate in chronic kidney disease
Authors: Do, Duyen Thi and Phan, Nam Nhut and Wang, Chih-Yang and Sun, Zhengda and Lin, Yen-Chang
Journal: Cytotechnology (2016): 2589--2604
Shear stress-induced alteration of epithelial organization in human renal tubular cells
Authors: Maggiorani, Damien and Dissard, Romain and Belloy, Marcy and Saulnier-Blache, Jean-Sébastien and Casemayou, Audrey and Ducasse, Laure and Grès, S and ra and Bellière, Julie and Caubet, Cécile and Basc and s, Jean-Loup and others
Journal: PloS one (2015): e0131416
Targeting a G-protein-coupled receptor overexpressed in endocrine tumors by magnetic nanoparticles to induce cell death
Authors: Sanchez, Claire and El Hajj Diab, Darine and Connord, Vincent and Clerc, Pascal and Meunier, Etienne and Pipy, Bernard and Payré, Bruno and Tan, Reasmey P and Gougeon, Michel and Carrey, Julian and others
Journal: Acs Nano (2014): 1350--1363
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 and Omi/HtrA2 induce annexin A2 cleavage followed by cell cycle inhibition and apoptosis
Authors: Wang CY, Lin YS, Su WC, Chen CL, Lin CF.
Journal: Mol Biol Cell (2009): 4153
Gold fluorescent annexin A5 as a novel apoptosis detection tool
Authors: Kurschus FC, Pal PP, Baumler P, Jenne DE, Wiltschi B, Budisa N.
Journal: Cytometry A (2009): 626
Detection of apoptosis induced by new type gosling viral enteritis virus in vitro through fluorescein annexin V-FITC/PI double labeling
Authors: Chen S, Cheng AC, Wang MS, Peng X.
Journal: World J Gastroenterol (2008): 2174
Evaluation of annexin V and Calcein-AM as markers of mononuclear cell apoptosis during human immunodeficiency virus infection
Authors: Palma PF, Baggio GL, Spada C, Silva RD, Ferreira SI, Treitinger A.
Journal: Braz J Infect Dis (2008): 108
Measurement of annexin V uptake and lactadherin labeling for the quantification of apoptosis in adherent Tca8113 and ACC-2 cells
Authors: Hu T, Shi J, Jiao X, Zhou J, Yin X.
Journal: Braz J Med Biol Res (2008): 750
Rhodamine B isothiocyanate doped silica-coated fluorescent nanoparticles (RBITC-DSFNPs)-based bioprobes conjugated to Annexin V for apoptosis detection and imaging
Authors: Shi H, He X, Wang K, Yuan Y, Deng K, Chen J, Tan W.
Journal: Nanomedicine (2007): 266